
Assisted Living vs. Independent Living : The Key difference is –
Assisted living is for seniors who need help with daily activities like bathing, dressing, or managing medications, while Independent living is for active seniors who can manage their daily routines independently.
Independent living focuses on convenience and lifestyle, offering services like housekeeping, meal plans, and social activities in private apartments or homes.
On the other hand, Assisted Living provides additional support, such as 24/7 assistance, personalized care, and access to healthcare professionals, ensuring safety and comfort for those who need it.
This detailed guide will explore the differences between these two for families and seniors to help them make informed decisions.
Independent living is designed for seniors who are generally healthy, active, and able to manage daily tasks without assistance. These communities emphasize a maintenance-free lifestyle, providing residents access to amenities, social activities, and conveniences that simplify life.
Assisted living is tailored for individuals who require help with daily living activities (ADLs) but do not need the intensive medical care provided by nursing homes. These communities blend housing, personal care, and health-related services in a supportive environment.
Independent living offers freedom and flexibility for those who can manage their day-to-day lives.
In contrast, Assisted living provides the necessary support for individuals who need help with personal care and daily activities.
Choosing between these options depends on a senior’s health, lifestyle preferences, and the required level of assistance.
For a better understanding, see this table. You will get a clear idea about these two.
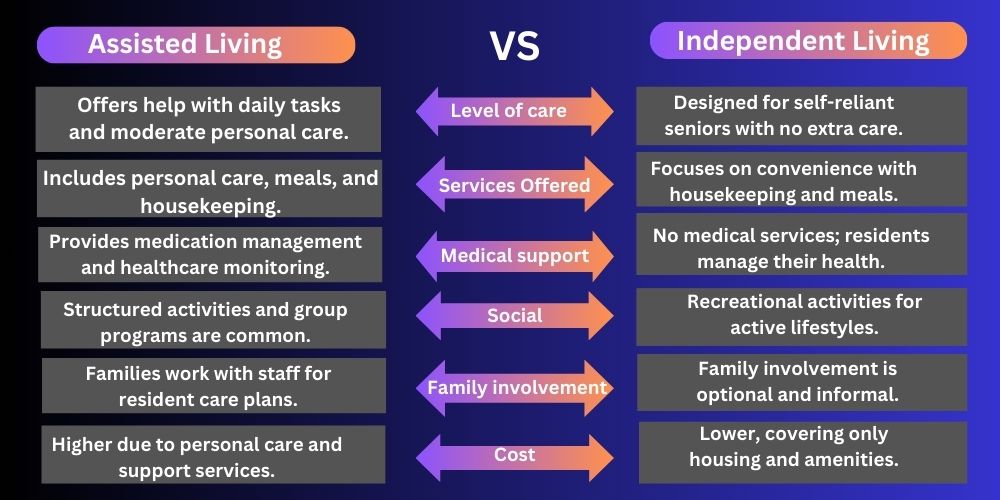
Let’s discuss this in detail below.
One of the most significant differences between assisted living and independent living is the level of care provided.
Independent Living:
Independent living is designed for still-active seniors who can manage their daily activities without assistance. It offers a lifestyle that prioritizes autonomy while eliminating the burdens of homeownership, such as maintenance, cooking, and cleaning. Seniors who choose independent living are typically healthy and do not require regular medical supervision.
Assisted Living:
Assisted living is intended for seniors who need help with daily tasks like bathing, dressing, managing medications, or mobility. It bridges the gap between independent living and skilled nursing care. Residents in assisted living receive personalized support tailored to their specific needs, ensuring they can maintain as much independence as possible while having access to necessary assistance.
Assisted and independent living offer thoughtfully designed housing options, but the arrangements cater to different lifestyles.
Independent Living:
Independent living communities typically feature private apartments, cottages, or homes designed with senior-friendly amenities, such as single-story layouts, grab bars in bathrooms, and emergency response systems. These homes offer privacy and independence, much like a traditional home, while providing access to communal amenities like dining areas, libraries, fitness centres, and gardens.
Assisted Living:
Assisted living communities provide more compact living spaces, often apartment-style units or shared accommodations. These homes are designed to be close to care staff and shared facilities to ensure assistance is always readily available. While residents maintain independence, the environment is structured to support safety and accessibility, with features like wheelchair ramps and emergency call systems.
The range of services available in these two living options varies significantly, reflecting the needs of their residents.
Independent Living:
The primary focus is on convenience and enhancing quality of life. Services commonly include:
These services allow seniors to focus on enjoying their retirement without the hassles of daily chores. However, independent living does not typically only provide personal care services.
Assisted Living:
In addition to the services offered in independent living, assisted living communities provide:
This comprehensive support ensures seniors receive the care they need while living in a comfortable and nurturing environment.
Healthcare and medical assistance are key differentiators between assisted and independent living.
Independent Living:
These communities do not provide medical care or assistance with health-related tasks. Residents are expected to manage their healthcare needs independently, though some communities might partner with external healthcare providers for additional services if required.
Assisted Living:
Assisted living offers more robust medical support, including:
Assisted living ensures peace of mind for seniors with chronic conditions or those recovering from illnesses by providing access to trained caregivers and medical oversight.
Cost is often a deciding factor when choosing between assisted and independent living.
Independent Living:
Independent living is generally more affordable than assisted living because it does not include personal or medical care. Costs vary based on location, community amenities, and housing type, but the price typically covers rent, utilities, meals, and recreational activities. Independent living costs range from $1,500 to $4,000 per month.
Assisted Living:
The higher cost of assisted living reflects the additional care and services provided. Monthly costs usually range from $3,000 to $7,000, depending on the level of care required, location, and community features. Most assisted living communities charge a base fee and additional charges for specific services like medication management or enhanced care.
Assisted and independent living emphasizes creating a vibrant, community-centred environment, but their social offerings cater to different lifestyles.
Independent Living:
These communities are designed to promote an active and social lifestyle. Residents can participate in:
Seniors living independently often have more freedom to organize their schedules and pursue personal interests.
Assisted Living:
While social opportunities are abundant in assisted living, the activities are often more structured and tailored to residents with varying physical and cognitive abilities. Common programs include:
Socialization in assisted living focuses on fostering connection and engagement while accommodating individual needs.
The suitability of each option depends on a senior’s health, independence, and lifestyle preferences.
Independent Living:
Assisted Living:
Assisted living is best for seniors who:
Choosing between assisted and independent living is a deeply personal decision that depends on the senior’s health, preferences, and financial situation. Families should consider factors such as the senior’s ability to manage daily tasks, the medical oversight needed, and the desire for independence versus support.
Both options share a common goal: enhancing the quality of life for seniors while providing a sense of community and belonging. Whether it’s the freedom of independent living or the personalized care of assisted living, these communities create environments where seniors can thrive during their golden years.
Visiting potential communities and discussing needs with care advisors can provide valuable insights for those still deciding which option is best. Ultimately, the right choice will prioritize safety, comfort, and happiness for seniors and their loved ones. Contact us at Arcticrosealf.com ,located in Wasilla, Alaska, to discuss your goal.
Assisted living provides support with daily activities like bathing, dressing, and medication management. In contrast, independent living is designed for seniors who can live independently without assistance but prefer a community-focused lifestyle.
People move to assisted living to receive help with daily tasks, ensure safety, reduce loneliness, and access healthcare services in a supportive environment while maintaining as much independence as possible.
Assisted living bridges the gap between independent living and nursing homes. It offers personal care and support without the intensive medical care in nursing homes, making it ideal for those needing moderate assistance.
Most seniors move into assisted living in their mid-to-late 70s or early 80s, often when they begin needing regular help with daily tasks or healthcare management.